Understanding Intel CPU Naming Scheme: 1st Gen upto 13th Gen CPU
Intel, the world-renowned chip manufacturer, has dominated the CPU market for decades. With each passing year, Intel introduces new and improved processors, often leaving consumers perplexed by the ever-evolving naming conventions. In this article, we will decipher the Intel CPU naming scheme to help you understand the significance of each element and make informed choices when selecting your next processor.
Intel CPU Brand Modifier: Core i9, Core i7, Core i5, Core i3
The first piece of the puzzle lies in the brand modifier, which indicates the performance tier of the processor. Intel typically releases processors under four primary brands:

- Core i9: Positioned at the top end, Core i9 CPUs offer the highest performance and are targeted at enthusiasts, content creators, and gamers seeking the best possible computing experience.
- Core i7: Positioned just below Core i9, Core i7 CPUs are high-performance processors offering exceptional power for demanding tasks and multitasking.
- Core i5: The Core i5 series caters to mainstream users and strikes a balance between performance and affordability, making it a popular choice for general-purpose computing and gaming.
- Core i3: Positioned as budget-friendly CPUs, Core i3 processors are suitable for everyday tasks and light productivity work.

Intel CPU Generation Number: 10th Gen, 11th Gen, etc.
The generation number is the next vital component of the naming scheme and represents the iteration of the microarchitecture used in the CPU. As Intel introduces new microarchitectures, they increment the generation number. Each new generation typically brings noticeable improvements in performance, power efficiency, and features.
Model Number: i7-10700K, i5-11600K, etc.
The model number provides more specific information about the processor’s respective brand and generation. The model number is constructed as follows:
- Brand Prefix: As discussed earlier, the brand prefix denotes the performance tier (e.g., i7 for Core i7).
- Generation Identifier: The first digit(s) following the hyphen in the model number indicate the generation of the processor (e.g., 10700 signifies a 10th Gen processor, 11600 denotes an 11th Gen processor).
- Performance Tier: The subsequent two digits provide additional information about the processor’s relative performance within its brand and generation. Higher numbers generally indicate better performance within the same series.
Suffix Letters
These optional letters represent specific features or characteristics of the processor.
- “K” indicates an unlocked multiplier for easy overclocking. non-K Intel desktop CPU means it only has limited overclocking capabilities.

- “H” often denotes high-performance graphics and it is used in mobile devices primarily gaming laptops.

- “U” and “Y” represents ultra-low power models used in laptops and other mobile devices. This is used for devices that focus more on battery life than performance.
- “T” indicates power-optimized models with lower TDP (Thermal Design Power). Because it is a low-powered CPU it is mostly used by all-in-one computers and small form factor computers that uses small power supplies and a weak/passive cooling system.
- “P” denotes Performance for thin & light. This kind of CPU is often used for ultrabook laptops
- “F” denotes models without integrated graphics. the processor you are buying does not have any integrated graphics chip. You will need to pair this with a discrete GPU to be able to out the video.

| Form/Function Type/Segment | Suffix | Optimized/Designed For |
|---|---|---|
| Desktop | K | High performance, unlocked |
| F | Requires discrete graphics | |
| S | Special edition | |
| T | Power-optimized lifestyle | |
| X/XE | Highest performance unlocked | |
| Mobile (Laptop2, 2 in 1) | HX | Highest performance, all SKUs unlocked |
| HK | High performance, unlocked | |
| H | High performance | |
| P | Performance for thin & light | |
| U | Power efficient | |
| Y | Extremely low-power efficient | |
| G1-G7 | Graphics level (processors with newer integrated graphics technology) | |
| Embedded | E | Embedded |
| UE | Power efficient | |
| HE | High performance | |
| UL | Power efficient, in LGA package | |
| HL | High performance, in LGA package |
For more info follow this link: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/processors/processor-numbers.html
Conclusion
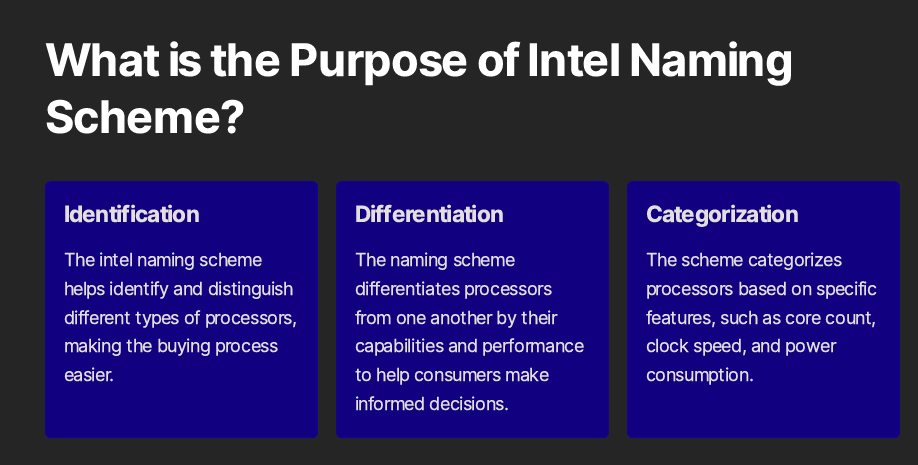
Understanding the Intel CPU naming scheme empowers consumers to make more informed decisions when purchasing processors. By deciphering the brand modifier, generation number, model number, and suffix letters, one can determine the performance level, capabilities, and target market of each CPU model. As technology advances and Intel continues to innovate, staying up-to-date with the latest naming conventions ensures you select the best CPU to suit your specific needs and budget. To access the latest information, always refer to Intel’s official website or consult reliable sources in the tech industry.
Disclaimer: This page contains links that are part of different affiliate programs. If you click and purchase anything through those links, I may earn a small commission at no extra cost to you. Click here for more information.
SUBSCRIBE TO TECHNOBRAX
If you want to receive updates whenever we post new articles or emails regarding discount deals on mice and keyboards, or other electronic devices CLICK HERE to SUBSCRIBE







